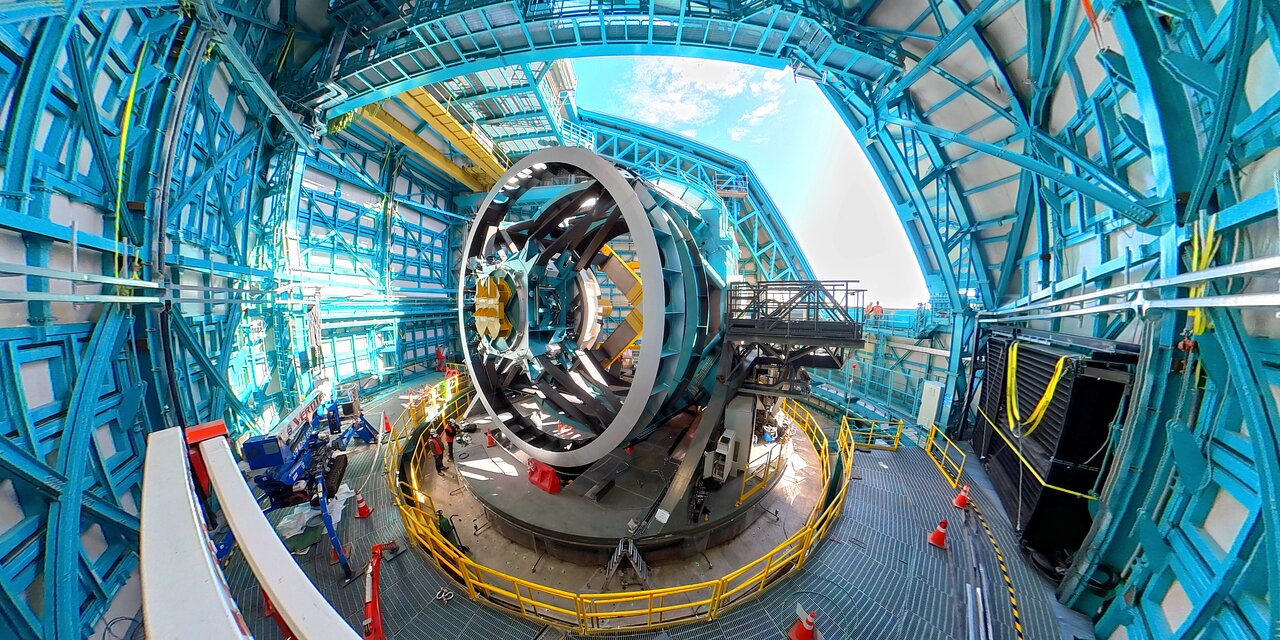
Nestled in the serene Andes Mountains of Chile, the Rubin Observatory stands at the forefront of modern astronomical research, unearthing the secrets of the universe. As part of the groundbreaking Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) project, this observatory is set to revolutionize our understanding of celestial phenomena with the help of its state-of-the-art LSST Camera. Designed to create a detailed map of the Milky Way, the observatory will conduct a comprehensive 10-year survey aimed at exploring elusive concepts such as dark matter. This ambitious NSF project is not just a significant stride in astrophysics; it’s a leap towards making vast amounts of astronomical data accessible to the global scientific community and the public alike. With an impressive engineering precision, the Rubin Observatory promises to illuminate some of the universe’s most profound mysteries while fostering educational initiatives for the next generation of scientists.
Located amid the picturesque Andes, the Rubin Observatory is a pivotal hub for astronomical exploration, poised to transform our grasp of the universe. This cutting-edge facility supports the ambitious Legacy Survey of Space and Time, a monumental initiative designed to chart the Milky Way with unprecedented detail using its advanced LSST Camera. By systematically observing the night sky for a decade, the observatory aims to unravel the complexities of dark matter and dark energy, key components that shape the cosmos. As a National Science Foundation-supported venture, it combines scientific inquiry with educational outreach, making raw data available to researchers and students worldwide. The Rubin Observatory not only represents a technological marvel in astrophysics but also serves as a beacon of collaboration in the quest to decode the cosmos.
Unveiling the LSST Camera: A Game-Changer in Astronomy
The LSST Camera represents a significant advancement in astronomical technology, designed to capture images of the night sky with unparalleled detail and scope. As the largest astronomical camera ever constructed, its design embodies a unique combination of large-aperture and wide-field capabilities, which allows it to observe countless faint celestial objects simultaneously. With this 144-megapixel test camera already operational, the LSST Camera promises images that are 21 times larger, pushing the boundaries of what astronomers can see and discover. This major leap forward is set to revolutionize cosmic cinematography, shedding light on phenomena that were previously too faint or distant for traditional telescopes to capture effectively.
The implications of the LSST Camera extend far beyond simply capturing breathtaking celestial images. By allowing astronomers to compile a time-lapse image of the sky every night, the camera can track dynamic events, such as the movement of asteroids or the emergence of supernovae, in real-time. This capability is essential to advancing our understanding of many cosmic phenomena while addressing fundamental questions concerning dark matter and dark energy. The data produced by the LSST Camera will provide researchers with invaluable insights, as it will cater to a broad array of scientific interests, ultimately reshaping how we approach astrophysics and cosmic exploration.
The Rubin Observatory: Mapping the Milky Way and Revealing Dark Matter
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, a NSF-funded project located in Chile, aims to create a comprehensive map of the Milky Way galaxy and beyond. With its advanced telescope and the LSST Camera, the observatory will conduct repeated sky scans, resulting in a detailed view of celestial changes over a decade. This unprecedented mapping effort will not only enhance our understanding of the Milky Way’s structure but also help illuminate the elusive nature of dark matter, which constitutes roughly 90% of the galaxy’s mass. By analyzing the gravitational effects of dark matter on surrounding celestial bodies, scientists hope to gather clues about its characteristics and distribution.
In tackling dark matter and dark energy, the Rubin Observatory is not just about mapping the universe, but also about redefining our approach to astrophysical research. This groundbreaking project invites community collaboration by providing immediate access to astronomical data, thereby fostering a culture of openness and inclusivity in scientific exploration. The broader field of view granted by the LSST Camera means that researchers can explore a variety of topics without the constraints of traditional, targeted observation. This paradigm shift not only enhances the potential for discovery but also empowers the next generation of scientists and students, promising to inspire future advancements in astrophysics.
Examining the Universe’s Mysteries with State-of-the-Art Technology
As a pioneering NSF project, the Rubin Observatory emphasizes the importance of sophisticated technology in understanding the cosmos. By integrating cutting-edge imaging equipment, such as the LSST Camera, the observatory prepares to tackle some of the most pressing questions in astrophysics today. The immense ability to observe the night sky on an unprecedented scale allows scientists to gather data that could potentially decode the ambiguities surrounding dark matter and dark energy. This technological leap fosters an environment where exploratory research can flourish, promising groundbreaking findings and advancements in our fundamental grasp of the universe.
Moreover, the observatory’s innovative approach means that the resulting data will not only be analyzed by professional astronomers but also made accessible for educational purposes. This effort aims to engage K-12 students and the general public, promoting a broader understanding of astronomical science and inspiring future generations to join the field of astrophysics. By involving a diverse audience in the discourse about dark matter, the Milky Way, and other cosmic mysteries, the Rubin Observatory seeks to create a community that is well-informed and excited about the cosmos, paving the way to vital scientific discoveries.
Cosmic Cinematography: A New Era in Astronomical Observations
The phrase ‘cosmic cinematography’ aptly encapsulates the innovative approach the Rubin Observatory is taking in observing the cosmos. By integrating advanced optical technology with a robust imaging system, the LSST Camera transforms the way astronomers view the universe, enabling them to gather visual data about dynamic and transient astronomical events. This capability takes advantage of the telescope’s large-aperture, wide-field design to produce sweeping panoramic images that reveal the hidden details of the night sky. As a result, it allows researchers to track temporal changes across vast stretches of space.
This unique observational technique is set to empower scientists not only in their quest to map the Milky Way but also in their mission to shed light on cosmic phenomena such as supernovae, gamma-ray bursts, and even the movement of previously undetected celestial bodies. By leveraging regular, high-resolution imagery, the Rubin Observatory will act as a time capsule, revealing changes in the cosmos over the course of a decade. This approach fundamentally alters our relationship with the universe, as it opens up new avenues for both personal exploration and academic investigation in the increasingly rich field of astrophysics.
The Legacy Survey of Space and Time: A Ten-Year Journey
The ambitious Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) is designed to span ten years, focusing on the systematic and comprehensive study of the night sky. The project’s methodology involves capturing vivid images every few nights, allowing it to build a continuously updated catalog of astronomical events. This commitment to long-term observation means that changes can be quantified and studied over an extended period, offering an opportunity to observe how celestial phenomena evolve over time. The depth and breadth of the LSST are expected to unearth insights into both immediate and distant cosmic events, enabling scientists to connect the dots between various astronomical occurrences.
Through the extensive dataset generated over the course of this decade-long quest, the Rubin Observatory aims to foster a collaborative scientific community. Researchers from various disciplines will be able to access and utilize the open data, leading to groundbreaking investigations of dark matter, dark energy, and the structure of the Milky Way. The emphasis on data openness and accessibility not only enhances the collaborative spirit but also enriches the educational landscape, as it encourages stakeholders from diverse backgrounds to engage in the exploration of the universe, fortifying the scientific inquiry and understanding of our cosmic home.
Dark Matter: Illuminating the Unknown
Dark matter remains one of the greatest mysteries in astrophysics, comprising an astonishing 90% of the Milky Way’s mass yet eluding direct detection. The Rubin Observatory’s advanced imaging capabilities offer a remarkable opportunity to explore this enigmatic substance. By observing the gravitational effects dark matter exerts on visible objects, researchers can infer its properties without needing to observe it directly. The LSST Camera’s precision and extensive coverage will enable scientists to monitor how light interacts with galaxies and clusters, providing critical data to decipher the elusive nature of dark matter.
The excitement surrounding the potential discoveries related to dark matter centers on the Rubin Observatory’s vision to redefine our understanding of the universe’s composition. With every image it captures, the LSST Camera plays a pivotal role in formulating theories related to dark matter’s distribution and influence. By inviting collaboration and making findings publicly accessible, the observatory ensures that researchers globally can contribute to unraveling this cosmic puzzle, paving the way for a deeper grasp of fundamental physics and our place in the universe.
Educational Outreach: Connecting Science and Community
A standout component of the Rubin Observatory’s mission is its commitment to education and outreach. Recognizing the importance of engaging future generations, the observatory partners with educational institutions to develop resources that make complex astrophysical concepts accessible to students from kindergarten through 12th grade. This initiative aims to inspire curiosity about astronomy, science, and the cosmos, fostering a love for exploration and discovery that can last a lifetime. Through interactive programs and open data, students can immerse themselves in real scientific inquiry, bridging the gap between theoretical concepts and tangible cosmic phenomena.
Involving the wider community enhances the impact of the Rubin Observatory’s findings, as the pursuit of knowledge does not rest solely in academic circles. By promoting public engagement with astronomy through exhibitions, workshops, and outreach programs, the observatory cultivates a collaborative environment where science thrives. This united approach bolsters not only a general understanding of dark matter and the Milky Way but also promotes appreciation for the importance of data-driven research in tomorrow’s scientific endeavors. Ultimately, the Rubin Observatory’s educational outreach embodies a forward-thinking strategy that prepares the next generation to tackle the questions of the cosmos.
Transforming Data into Knowledge: The Role of Open Access
As part of its mission, the Rubin Observatory emphasizes the value of open access to the immense amounts of data generated by its observations. By providing unrestricted access to this wealth of information, the observatory facilitates a culture of sharing that allows both professional researchers and amateur enthusiasts to participate in the scientific exploration of the universe. This paradigm shift not only democratizes access to astronomical resources but also enables innovative collaborations across global scientific communities. Every observation captured by the LSST Camera can become a catalyst for new research, enhancing our understanding of the cosmos.
Open access to data empowers scientists to validate findings, explore new hypotheses, and develop tools that further astronomical research. The comprehensive dataset produced by over a decade of intense observation will allow researchers to track changes in the sky, investigate dark matter distributions, and analyze the Milky Way’s dynamics. This concerted effort ensures that knowledge isn’t confined within institutional boundaries—it’s a collective journey toward enlightening mysteries that have perplexed humanity for centuries. Together, through collaboration and shared resources, scientists can paint a clearer picture of our universe and its myriad wonders.
The Future of Astrophysics: Exploring New Frontiers
Looking ahead, the Rubin Observatory stands at the forefront of a new era in astrophysics, poised to unravel some of the universe’s most profound mysteries. With its unique capabilities, the observatory will enable groundbreaking discoveries about dark matter and dark energy—the fundamental components that shape our cosmic landscape. As the observatory evolves, it embraces a vision not only to collect data but also to generate insights that will influence future research and policy decisions in scientific communities worldwide.
In pursuing these ambitious goals, the Rubin Observatory fosters a collaborative network where astronomers, physicists, and educators converge to share knowledge and tackle the pressing questions of our time. The enduring commitment to openness ensures that discoveries are disseminated broadly, creating a culture of inquiry and participation. The universe is more accessible than ever before, inviting all to explore, question, and ultimately understand the vastness and complexities hidden within the night sky. As we await the fruits of this monumental NSF project, the excitement surrounding the potential discoveries continues to soar.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Rubin Observatory and its significance in astrophysics?
The Rubin Observatory, also known as the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, is a groundbreaking NSF project designed to conduct the 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST). It aims to create a comprehensive map of the universe, focusing on various astrophysical phenomena including dark matter, by capturing a time-lapse image of the night sky every night.
How does the LSST Camera enhance the capabilities of the Rubin Observatory?
The LSST Camera is the largest astronomical camera ever constructed, capable of acquiring images 21 times larger than those from the test camera. By integrating this advanced camera with the Simonyi Survey Telescope at the Rubin Observatory, researchers will be able to observe numerous faint cosmic objects simultaneously, thereby deepening our understanding of dark matter and the Milky Way.
When can we expect the first astronomical images from the Rubin Observatory?
The first public release of astronomical images from the Rubin Observatory is expected in mid-2025, following a commissioning period of approximately six months after the installation of the LSST Camera, which is set to become operational by the end of January 2025.
What role does the Rubin Observatory play in mapping the Milky Way?
The Rubin Observatory is pivotal in mapping the Milky Way by capturing detailed images of its structure and dynamics over a 10-year period. This continuous sky surveillance, enabled by the LSST Camera, will facilitate the discovery of new stars, galaxies, and other celestial phenomena, thereby enhancing our understanding of the Milky Way.
What are the major scientific goals of the Rubin Observatory project?
The major scientific goals of the Rubin Observatory include mapping dark matter and dark energy, observing rapidly changing celestial events, and detecting potentially hazardous asteroids. By utilizing its advanced imaging capabilities, the observatory aims to provide valuable insights into these fundamental astrophysical questions.
How is the data from the Rubin Observatory shared with the scientific community?
The data collected by the Rubin Observatory will be immediately available to the entire scientific community and the public. This innovative approach promotes open data sharing and educational outreach, ensuring that both formal astronomical research and informal education can benefit from the findings of this groundbreaking NSF project.
What advancements in technology are emphasized by the Rubin Observatory’s LSST Camera?
The LSST Camera emphasizes advancements in technology that facilitate ‘cosmic cinematography’—capturing wide-field, large-aperture images of celestial objects. Its precision enables researchers to study dark matter and energy with unprecedented detail, thereby pushing the boundaries of current astrophysical research.
What impact could the Rubin Observatory have on our understanding of dark energy?
The Rubin Observatory could significantly enhance our understanding of dark energy by providing high-resolution data that allows scientists to study its effects on the universe’s expansion. By capturing extensive astronomical data over a decade, researchers hope to uncover new insights into the nature of this elusive force.
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Rubin Observatory | Home to the Simonyi Survey Telescope and the 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time project. |
| Commissioning Camera | 144-megapixel test camera capturing initial images of the night sky. |
| LSST Camera | The largest astronomical camera ever constructed, 21 times bigger than the test camera. |
| Open Data Philosophy | Plans to release all data to the scientific community and K-12 education. |
| Cosmic Cinematography | Combines wide-field and large-aperture capabilities to observe many faint objects simultaneously. |
| Dark Matter & Dark Energy Research | Aims to explore these phenomena with unprecedented resolution. |
| 10-Year Duration | The project’s timeline focuses on comprehensive mapping and observation of cosmic phenomena. |
Summary
Rubin Observatory is set to revolutionize our understanding of the universe with its ambitious 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time project. By leveraging advanced technology like the LSST camera, the observatory will provide unprecedented insights into dark matter, dark energy, and various celestial phenomena, all while ensuring open data access for the scientific community and educational outreach. This groundbreaking initiative marks a pivotal moment for astronomical research, offering a dynamic approach to studying our cosmos.